The Comprehensive Guide to Truckload Shipping: Understanding Options, Costs, and Services
The truckload shipping industry is evolving rapidly, presenting a myriad of choices and cost considerations for businesses across the globe. This comprehensive guide explores the different truckload shipping options available, how to estimate costs, and the nuances of working with freight brokers versus asset-based carriers. Read on to gain a deeper understanding of truckload shipping services and what factors impact your shipping costs. Contact us today if you need FTL Shipping Service.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Hook
- Context
- Purpose
- Background/Industry Overview
- Current State
- Historical Context
- Truckload Shipping Options
- Dry Van
- Reefer
- Flatbed
- Intermodal
- Weight Capacity and Skid Information
- Truckload Capacity
- Skid Configuration
- Freight Brokers vs. Asset-Based Carriers
- Definitions
- Pros and Cons
- Understanding Truckload Shipping Rates
- Factors Affecting Rates
- Rate Comparisons
- Common Truckload Shipping Questions
- Answers to Top 5 Questions
- Tools and Resources for Shipping Quotes
- Comparison Sites
- Estimating Costs
- Conclusion
- Summary
- Call to Action
- Final Thoughts
- Additional Sections
- Resources
- Glossary
Introduction
Hook: Did you know that choosing the right truckload shipping method could drastically impact your supply chain efficiency and costs? Whether you’re a business owner or logistics manager, understanding the intricacies of truckload shipping can lead to significant cost savings and operational improvements.
Context: In today’s fast-paced logistics environment, making informed decisions about truckload shipping is crucial. With various shipping options available, understanding each method’s benefits, capacities, and cost implications is essential for optimizing your supply chain.
Purpose: This guide aims to educate readers on the different truckload shipping options, clarify the differences between freight brokers and asset-based carriers, and provide insights into the factors that affect shipping rates. By the end, readers will be well-equipped to make informed shipping decisions and understand how to navigate the complexities of truckload shipping services.
Background/Industry Overview
Current State: The truckload shipping industry is a cornerstone of logistics and transportation in the United States. With advancements in technology and changing market demands, the industry has seen significant growth and transformation. Major players include logistics companies, freight brokers, and asset-based carriers, each playing a crucial role in the supply chain.
Historical Context: Truckload shipping has evolved from a primarily regional service to a sophisticated network capable of handling national and international logistics. Over the decades, innovations in transportation technology, regulatory changes, and shifts in market dynamics have shaped the current landscape.
Truckload Shipping Options
Dry Van: A dry van is the most common type of truck used for shipping. It is a fully enclosed trailer that protects cargo from weather conditions. Dry vans are ideal for transporting non-perishable goods, and they offer a high degree of security for valuable or sensitive items.
Reefer: Refrigerated trailers, or reefers, are designed to transport perishable goods that require temperature control. These trailers are equipped with cooling units to maintain the necessary temperature, making them suitable for shipping food products, pharmaceuticals, and other temperature-sensitive items.
Flatbed: Flatbed trucks have an open bed and are used for transporting oversized or irregularly shaped cargo. They are ideal for shipping construction materials, machinery, and other large items that do not fit into standard enclosed trailers.
Intermodal: Intermodal shipping involves using multiple modes of transportation, such as trucks and trains, to move cargo. This method offers flexibility and can be cost-effective for long-distance shipping. It is often used for large volumes of goods that need to be transported over long distances.
Weight Capacity and Skid Information
Truckload Capacity: The typical weight capacity for a truckload is around 45,000 to 48,000 pounds. However, this can vary based on the type of truck and the specific regulations in different states. For example, a standard 53-foot trailer can usually handle up to 26 pallets or skids.
Skid Configuration: A standard skid or pallet measures 40×48 inches. Depending on the truck’s configuration, a standard 53-foot dry van can accommodate approximately 26 to 30 skids. Reefer trailers and flatbeds may have different capacities based on their design and intended use.
Freight Brokers vs. Asset-Based Carriers
Definitions:
- Freight Broker: A freight broker acts as an intermediary between shippers and carriers. They have a network of carriers and can help shippers find the best transportation options for their needs. Brokers typically do not own trucks but facilitate transactions and manage logistics.
- Asset-Based Carrier: An asset-based carrier owns and operates its fleet of trucks. They are responsible for the entire transportation process, from pick-up to delivery. Asset-based carriers offer direct control over logistics and often provide more consistent service.
Pros and Cons:
- Freight Brokers:
- Pros: Broad network, flexibility in finding carriers, often lower costs.
- Cons: Less control over the transportation process, potential for variable service quality.
- Asset-Based Carriers:
- Pros: Direct control over fleet, consistent service, often better handling of special requirements.
- Cons: Limited flexibility, potentially higher costs due to owning and maintaining a fleet.
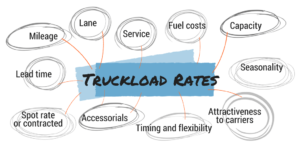
Understanding Truckload Shipping Rates
Factors Affecting Rates: Several factors influence truckload shipping rates, including distance, cargo weight, type of trailer, and current market conditions. Additional considerations include fuel prices, seasonal demand, and the level of service required.
Rate Comparisons: To get accurate rate comparisons, you can use tools like the FTL Shipping Service rate calculators. For instance, you can obtain a truckload freight quote in New York or compare FTL Shipping Rates in New Jersey to get a better understanding of the pricing in different regions.
Common Truckload Shipping Questions
Based on frequently asked questions, here are the top five concerns related to truckload shipping:
- What is truckload shipping?
- Truckload shipping involves transporting large quantities of goods using a dedicated truck. This method is ideal for shipments that require an entire truck’s capacity.
- How do I get a truckload freight quote?
- Obtain a truckload freight quote by contacting carriers or brokers, or using online tools to get estimates based on your shipment’s details.
- What factors affect truckload rates?
- Factors include the distance of the shipment, weight and volume of the cargo, type of truck required, and market conditions.
- How does FTL differ from LTL shipping?
- FTL Shipping means the entire truck is used for one shipment, whereas LTL (Less Than Truckload) involves sharing truck space with other shipments.
- What are the benefits of using a freight broker?
- Freight brokers offer access to a wide network of carriers, potentially lower costs, and can handle logistics and paperwork on your behalf.
Tools and Resources for Shipping Quotes
To get a precise estimate of shipping costs, use online tools like those available on FreightRun. These tools can provide a Freight Quote for TL or Truckload Shipping Cost based on your specific requirements. Additionally, exploring comparison sites helps you understand the Full Truckload Shipping Estimate and find the best Full Load Freight Quote.
Conclusion
Summary: Understanding the different truckload shipping options, capacities, and rate factors is crucial for making informed decisions. Whether you opt for a dry van, reefer, flatbed, or intermodal solution, knowing your needs and the services available can optimize your logistics and reduce costs.
Call to Action: Explore online tools for shipping quotes and consult with freight brokers or asset-based carriers to find the best solution for your needs. Engaging with industry experts and utilizing comparison sites can further enhance your decision-making process.
Final Thoughts: As the truckload shipping industry continues to evolve, staying informed about new trends and technologies will be key to maintaining a competitive edge in logistics and transportation.
Additional Sections
Resources:
Glossary:
- Dry Van: An enclosed trailer used for shipping non-perishable goods.
- Reefer: A refrigerated trailer used for transporting temperature-sensitive items.
- Flatbed: An open-bed truck used for oversized or irregular cargo.
- Intermodal: A shipping method involving multiple modes of transportation.
By understanding these elements, you can make more informed choices about your required FTL Shipping Service, ensuring efficiency and cost-effectiveness in your logistics operations.